| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||


|
|
|||
|
Departments of Alsace Overview(Alsatian: Elsàss; German: Elsass, pre-1996: Elsaß; Latin: Alsatia) Alsace {al-sas'} is an historic French region and former province with an area of 3,197 mi2 (8,280 km2) and a population of 1,852,325 based on the last official census in 2011. It is located in eastern France, across the Rhine River from Germany. Containing the departments of Bas-Rhin and Haut-Rhin, Alsace is bordered by the regions of Franche-Comté (southwest) and Lorraine (west), Germany (north), the Territory of Belfort and Switzerland (south). Much of the region consists of an alluvial plain lying between the Rhine and the steeply rising Vosges mountains, an especially fertile area where such crops as grapes, sugar beets, tobacco, and hops are grown. There are potassium mines and textile mills in the Mulhouse-Colmar areas, hydroelectric facilities at Kembs and Ottmarscheim, and a nuclear power plant at Fessenheim. Wine and beer are produced in the region. Alsace's capital and its chief industrial hub is Strasbourg, in which is located the famous Strasbourg Cathedral. Major manufactures are electrical appliances, chemicals, and textiles. The region's predominant language is French, with considerable German dialect (known as Alsatian) spoken; about three-quarters of the population are Roman Catholic. HistoryThe area that is now Alsace was occupied by Julius Caesar's legions in the 1st century BC. It was a thoroughly Roman region until the AD 5th-century arrival of the Alemanni. When this tribe was conquered by Clovis and the Franks in 496, Alsace was named a Frankish duchy, and later it was incorporated into the Carolingian empire and was Christianized. When the empire collapsed, Alsace became part of Lotharingia (843). The region became German as a component of the Duchy of Swabia in 870 when Lotharingia was divided between France's Charles II (Charles the Bald) and Germany's Louis the German. Under the aegis of the Holy Roman emperors, Alsace attained considerable self-determination, its 10 major cities flourishing as free imperial cities. During the 16th century the influence of France in the region became marked. Nonetheless, Alsace remained a part of the Holy Roman Empire until the 17th century. The region was a hotbed of Reformation ferment, but Protestantism was largely suppressed by the Habsburgs. During the Thirty Years' War, Alsatian cities appealed to France for aid, and France was given a protectorate over Alsace by terms of the Peace of Westphalia (1648). Complete French control over the area (with the exception of Belfort) was established in 1681, and it was officially incorporated into France during the Revolutionary era (1789). Alsace had by the beginning of the 19th century become almost completely Frankified. Nonetheless, after the Franco-Prussian War (1870-71), Alsace was annexed by Germany as part of Alsace-Lorraine. In an international see-saw, Alsace became French again after World War I (1918) under the terms of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles (see Paris Peace Conference), but fell to German troops in 1940 during World War II. The region again became part of France after its liberation by French and American forces in 1945. ClimateAlsace has a semi-continental climate with cold, dry winters and hot summers. A study of interannual rainfall during the period of 1971-1990, conducted by the Rhine-Meuse agency, shows that precipitation is very unevenly distributed in Alsace. The Vosges mountains receive rainfall at a rate greater than 39.4 inches (1000mm) per year, while a majority of the plains receive less than 27.6 inches (700mm) annually. The Colmar region, famous for its vineyards, is perhaps the best example anywhere in France of an important rainfall gradient. While the city itself receives only 21.7 inches (550mm), an area just 15 miles (25km) west of Colmar gets about 43.3 inches (1100mm) a year. The Rhine Valley's typical geography and the principal wind directions (mainly southwest-northeast or northeast-southwest) explain this uneven distribution of rainfall (known as the Foehn Effect). Timeline
Transportation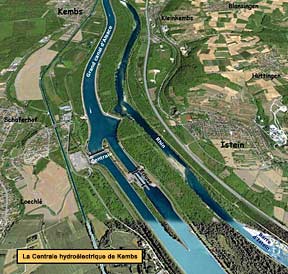
Aerial view of the Grand Canal d'Alsace and surrounding countryside, beside the communities of Kembs, Schaeferhof, and Loechlé. Note the locks (fr. écluse), a hydroelectric power plant (Centrale de Kembs), and the neighboring Rhine River. (click to enlarge) Grand Canal d'AlsaceThe Grand Canal of Alsace (French: Grand Canal d'Alsace, German: Rheinseitenkanal) is a canal in eastern France, channeling the Upper Rhine river. It is about 30 miles (50 km) long between Kembs and Vogelgrun, and provides access to the region from the Rhine River, Basel in Switzerland, and the North Sea for barges of up to 1,350 metric tons. The Grand Canal is larger than the Suez Canal and permits the navigation of more than 30,000 boats a year between Basel and Strasbourg. Construction of the canal began in 1932 and was completed after World War II in 1959. The canal diverts much of the water from the original bed of the fast-flowing Rhine in this area, which is almost entirely unnavigable by boats. The Grand Canal produces hydroelectric power at Kembs, Ottmarsheim, Fessenheim and Vogelgrun, supplying electricity to one of the most heavily industrialized regions in France and even to Germany. Furthermore, the canal provides enough water throughout the year to a nuclear power plant at Fessenheim, eliminating the need for cooling towers.
Sources: 2001 Grolier Multimedia Encyclopedia, ©2000 Grolier Interactive Inc. Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Population figures from INSEE, Institut National de la Statistique et des Études Économiques (the French National Institute for Statistics and Economic Studies). Precipitation statistics from CRDP (Centre Régional de Documentation Pédagogique de l'Académie de Strasbourg). All Rights Reserved. Images: Skyline of Strasbourg, © Corbis/Nik Wheeler. Maison des Tanneurs, former seat of the tanners' guild (Strasbourg), Sue Waugh (photographer), from Flibbertigibbet. A night-time view of the Petite-France district in Strasbourg, Mihai-bogdan Lazar (photographer, September 2011), from Dreamstime Stock Photos. Aerial view of the Grand Canal d'Alsace and surrounding countryside..., from Encyclopédie B&S Éditions. All Rights Reserved. NEXT PAGE » Languages, Traditional Costumes, and Cuisine of Alsace |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||